-40%
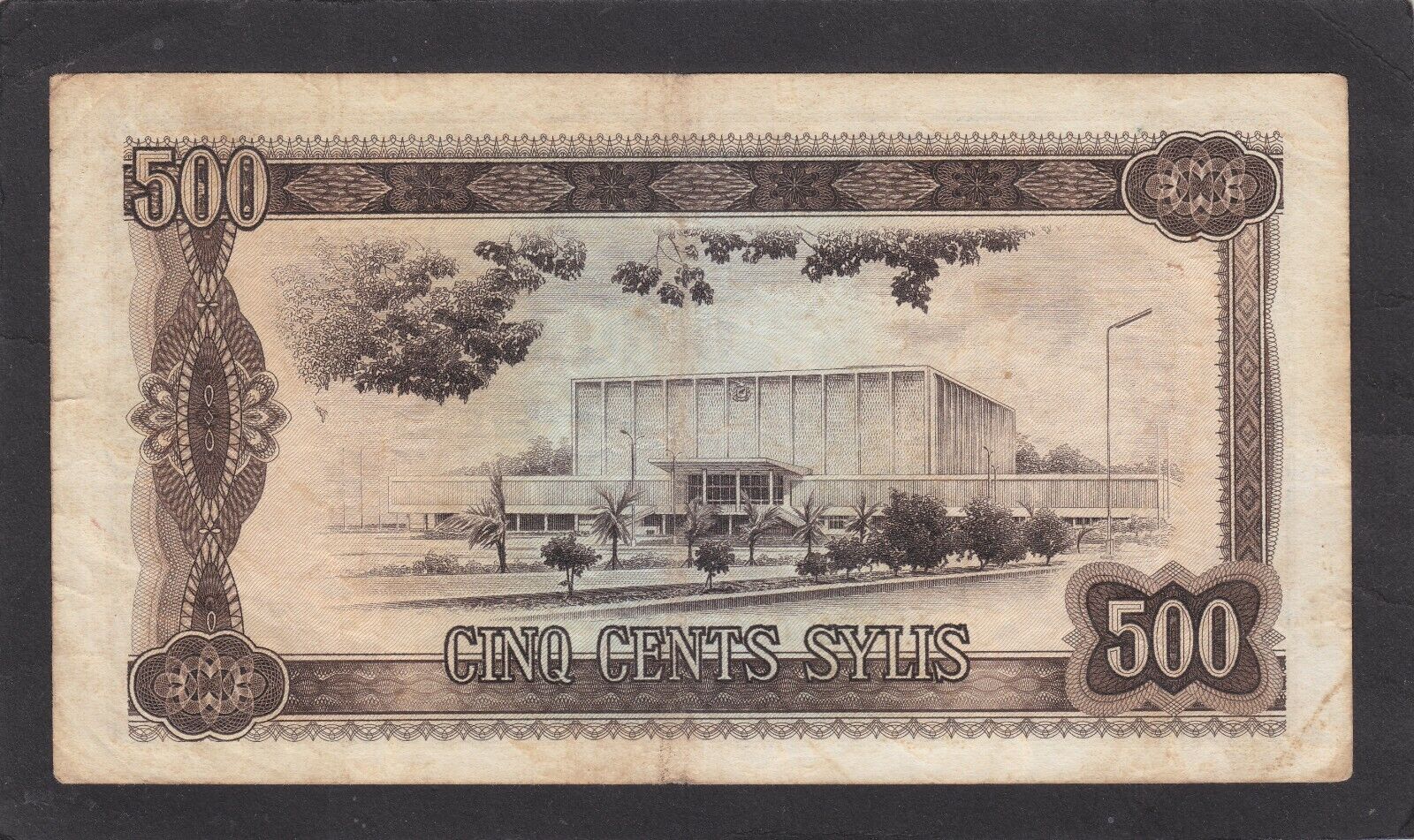
Guinea 500 Sylis 1980 P-27a VG stains
$ 3.69
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
One banknote ofGuinea 500 Sylis 1980 P-27a .Condition (opinion): Very Good (VG),stains ,see scan.
Portrait:Tito (Josip Broz Tito)
.Size:17 cm / 9,3cm (large).See related information from the web below.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Postage, including packing material, handling fees : Europe: USD 6.40 / USA $ 7.30. Rest of the World: USD 8.90
FREE of postage for any other items.
Only one shipping charge per shipment (the highest one) no matter how many items you buy (combined shipping).
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Guaranteed genuine -
One
month
return
policy
(retail sales) .
Returns accepted with no questions.
Customers are invited to combine purchases to save postage.
Full refund policy ,including shipping cost, guaranteed in case of lost or theft after the completion of the complaint with Spanish Correos for the registered letters
(free of extra charges for purchases abobe .00 or with the extra charge paid for purchases below .00).
As we have (or could have) more than one identical item ,the serial number may differ from those shown in the picture which is for reference only.
For purchases above .00 we send the orders registered with tracking number without extra charge, for purchases below .00 we ship as regular letters at the buyer's risk.
For purchases below $ 70,00 who want to register your letter with tracking number, please add an extra for : Europe .50 , U.S. .50 ,Rest of the word .30 .For this case ,please request or wait for our invoice before paying.
For some destinations and purchases below .00 customers may be requested for this extra shipping payment in order to register the shipment with tracking number.
We reserve the right to cancel transactions that require the sending of unregistered letters (without tracking number) to some destinations when this extra payment has been requested.
If for any reason, your item did not arrive yet, or you are not 100% satisfied with the item you have received, please do not hesitate to contact , I will do all it takes to provide the best service.
Banknote Grading
UNC
AU
EF
VF
F
VG
G
Fair
Poor
Uncirculated
About Uncirculated
Extremely Fine
Very Fine
Fine
Very Good
Good
Fair
Poor
Edges
no counting marks
light counting folds OR...
light counting folds
corners are not fully rounded
much handling on edges
rounded edges
Folds
no folds
...OR one light fold through center
max. three light folds or one strong crease
several horizontal and vertical folds
many folds and creases
Paper
color
paper is clean with bright colors
paper may have minimal dirt or some color smudging, but still crisp
paper is not excessively dirty, but may have some softness
paper may be dirty, discolored or stained
very dirty, discolored and with some writing
very dirty, discolorated, with writing and some obscured portions
very dirty, discolored, with writing and obscured portions
Tears
no tears
no tears into the border
minor tears in the border, but out of design
tears into the design
Holes
no holes
no center hole, but staple hole usual
center hole and staple hole
Integrity
no pieces missing
no large pieces missing
piece missing
piece missing or tape holding pieces together
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Marshal Josip Broz Tito (born Josip Broz; Serbo-Croatian pronunciation: [jɔ̌sip brɔ̂ːz tîtɔ]; Јосип Броз Тито; 7 May 1892[nb 1] – 4 May 1980) was a Yugoslav revolutionary and statesman, serving in various roles from 1943 until his death in 1980.[8] During World War IIhe was the leader of the Partisans, often regarded as the most effective resistance movement in occupied Europe.[9][10] While his presidency has been criticized as authoritarian,[11][12][13] Tito was "seen by most as a benevolent dictator"[14] due to his successful economic and diplomatic policies and was a popular public figure both in Yugoslavia and abroad.[15] Viewed as a unifying symbol,[16]his internal policies successfully maintained the peaceful coexistence of the nations of the Yugoslav federation. He gained international attention as the chief leader of the Non-Aligned Movement, working with Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Gamal Abdel Nasserof Egypt and Sukarno of Indonesia.[17]
He was General Secretary (later Chairman of the Presidium) of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (1939–80), and went on to lead the World War II Yugoslav guerrilla movement, the Partisans (1941–45).[18] After the war, he was the Prime Minister (1943–63),President (later President for Life) (1953–80) of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). From 1943 to his death in 1980, he held the rank of Marshal of Yugoslavia, serving as the supreme commander of the Yugoslav military, the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA). With a highly favourable reputation abroad in both Cold War blocs, Josip Broz Tito received some 98 foreign decorations, including the Legion of Honour and the Order of the Bath.
Josip was born as the seventh child to Croat father Franjo Broz and Slovene mother Marija Javoršek in the village of Kumrovec inCroatia. Drafted into military service, he distinguished himself, becoming the youngest Sergeant Major in the Austro-Hungarian Army.[19] After being seriously wounded and captured by the Imperial Russians during World War I, Josip was sent to a work camp in the Ural Mountains. He participated in the October Revolution, and later joined a Red Guard unit in Omsk. Upon his return home, Broz found himself in the newly established Kingdom of Yugoslavia, where he joined the Communist Party of Yugoslavia (KPJ).
Tito was the chief architect of the second Yugoslavia, a socialist federation that lasted from 1943 to 1991–92. Despite being one of the founders of Cominform, he was also the first (and the only successful) Cominform member to defy Soviet hegemony. A backer of independent roads to socialism (sometimes referred to as "national communism"), he was one of the main forces behind the Non-Aligned Movement, and its first Secretary-General. He supported the policy of nonalignment between the two hostile blocs in the Cold War. Such successful diplomatic and economic policies allowed Tito to preside over the Yugoslav economic boom and expansion of the 1960s and 1970s.[20][21][22] His internal policies included the suppression of nationalist sentiment and the promotion of the "brotherhood and unity" of the six Yugoslav nations. After Tito's death in 1980, tensions between the Yugoslav republics emerged and in 1991 the country disintegrated and went into a series of civil wars and unrest that lasted the rest of the decade and continue to impact most of the former Yugoslav republics. He remains a controversial figure in the former Yugoslavian republics.